Podemos
The Spanish and European establishments have just days to stop the advance of the progressive electoral alliance United We Can in the June 26 general elections in the Spanish state. How are they doing? As matters stand, not well.
United We Can, formed in early May, brings together new anti-austerity party Podemos and the longer-standing United Left (IU), as well as broader coalitions in Catalonia (Together We Can), Galicia (In Tide) and Valencia (A La Valenciana).
 United We Can.
United We Can — the united ticket made up of Podemos, the United Left, the green party Equo and three broader alliances in Catalonia, Galicia and the Valencian Country — is campaigning in the June 26 Spanish general elections on a plan to reverse economic austerity.
United We Can.
United We Can — the united ticket made up of Podemos, the United Left, the green party Equo and three broader alliances in Catalonia, Galicia and the Valencian Country — is campaigning in the June 26 Spanish general elections on a plan to reverse economic austerity.
Five months after the December 20 election in Spain failed to produce a government, the country is returning to the polls in the most polarised contest since the end of the Franco dictatorship in 1977.
 United Left leader Alberto Garzon and Podemos leader Pablo Iglesias celebrating the formation of an alliance between the two parties.
Spain's anti-austerity party Podemos and older left-wing party United Left announced on May 9 that they had reached a preliminary agreement to run on a joint platform before Spain's new general election on June 26.
United Left leader Alberto Garzon and Podemos leader Pablo Iglesias celebrating the formation of an alliance between the two parties.
Spain's anti-austerity party Podemos and older left-wing party United Left announced on May 9 that they had reached a preliminary agreement to run on a joint platform before Spain's new general election on June 26.
Four lawmakers from Spain's far-left Podemos party and its allies are participating in a week-long hunger strike to try to rally public support for refugees.
The lawmakers began their hunger strike on April 16 and called on people to occupy public squares for 24 hours on April 22, the day their actions end. The hunger strike is a gesture of support for those people at the center of Europe's biggest migrant crisis since World War II.
Twenty-four hour assemblies were planned for a dozens cities on April 22.
 All media outlets in the Spanish state were dominated by the images of two men on March 1: one was leaving jail near the northern city of Logrono to the cheers of inmates he was leaving behind; the other was trying to convince the Spanish parliament in Madrid to vote him in as prime minister.
All media outlets in the Spanish state were dominated by the images of two men on March 1: one was leaving jail near the northern city of Logrono to the cheers of inmates he was leaving behind; the other was trying to convince the Spanish parliament in Madrid to vote him in as prime minister.
Since Spain's December 20 elections produced no clear majority, debate has raged over what sort of government should be formed.
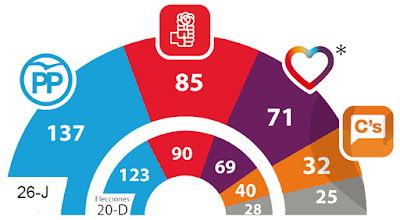
The governing conservative People's Party (PP) won 123 seats in the 250-seat Congress and the right-populist Citizens won 40. On the left, the main opposition Spanish Socialist Workers Party (PSOE) won 90 seats, while radical anti-austerity party Podemos and the three alliances in which it took part together with nationalist forces won 69.
What was the central message of the December 20 Spanish general elections, which was “won” by the governing conservative People's Party (PP) of Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy with only 28.72% of the vote, 3.6 million votes less than the last national poll in 2011?
Why did the opposition Spanish Socialist Workers Party (PSOE) greet its worst ever result —22.01%, 1.4 million votes less than 2011 — with a sigh of relief?
 Podemos activists
The December 20 elections in the Spanish state will attract the usual large field of runners. Challengers will represent every imaginable position along the Spanish state's two main political dimensions — the left-to-right social axis and the axis of national rights.
This second dimension reaches from the centralism of the ruling People's Party (PP) to the pro-independence stance of various Catalan, Basque and Galician parties.
Podemos activists
The December 20 elections in the Spanish state will attract the usual large field of runners. Challengers will represent every imaginable position along the Spanish state's two main political dimensions — the left-to-right social axis and the axis of national rights.
This second dimension reaches from the centralism of the ruling People's Party (PP) to the pro-independence stance of various Catalan, Basque and Galician parties.
Members of the European Parliament show support for Greece against its creditors. "This debate is not exclusively about one country," said the Greece's left-wing Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras in a speech to the European Parliament on July 8. "It is about the future of our common construction."
Regional elections held in Spain on May 24 installed an historic pro-Basque state government in the Basque autonomous community of Navarre for the first time. It ended 16 years of rule by the pro-Spanish, centre-right Navarrese People's Union (UPN).
The UPN won only 15 seats, down four from 2011. Its ally, the right-wing Spanish People’s Party (of Spanish Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy), won two, half of its quota in 2011.
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page





